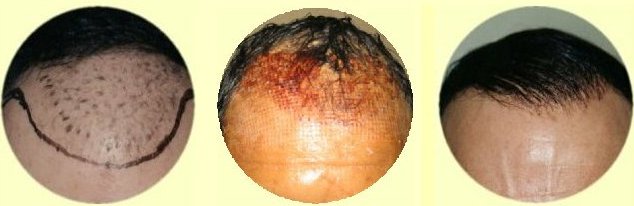
2- Scalp & hair color
3- Curliness
4- Texture (Caliber)
5- Density
6- Amount of donor hair
Hair follicle
transplantation is the most up-to-date method to manage androgenic baldness
in males as well as deficient hair density in females. It is the backbone
of hair restoration surgery and it is now the primary treatment in all
cases of Male Pattern Baldness.
Hair transplantation is based on the concept of "donor dominance" in Male Pattern Baldness (MPB). If a graft is taken from an area destined to be permanently hair bearing and is transplanted into an area of MPB or future MPB, it will after an initial short period of effluvium, continue to grow hair in its new site. Thus all planning of redistribution of permanent hair is predicated on an accurate assessment of the ultimate extent of alopecia and its counterpart, the permanent donor rim
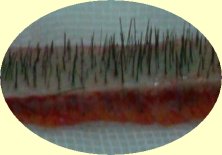
In the 1990s the concept of follicular unit has revolutionized hair transplantation. Human hair emerges from the scalp in groupings known as follicular units.
Follicular unit transplantation is a method of hair restoration surgery where hair is transplanted in its naturally occurring individual follicular unit. This led to the use of smaller micrografts and finally single hair transplants. Using different-sized smaller grafts helps avoiding the corn rowing "the doll's head appearance" and dramatically improves results
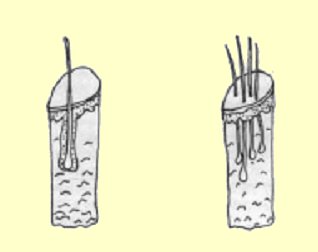
There are three types of hair micrografts
Single hair
follicular unit & Single follicular unit (for
hairline resotration) Offer more natural
look, However yield lesser number of grafts
-- Single
Hair Follicular Units: Used
primarily for the hairline area to create a softer more natural appearance.
-- Single
Follicular Units consisting of 2-3 hairs:Used
right behind the hairline to create a more dense appearance
Modified follicular unit consisting of about 3-4 hairs Used primarily for adding density to the recipient area. They provide a thicker, fuller appearance, and are more suited to the non-hairline regions of the scalp.
Sessions
Megasessions
of thousands of these three types of Follicular unit in a single sitting
and dense packing of the bald area is the best solution to accomplish the
maximum result in the least number of sessions, The number of sessions
needed vary according to the extent of baldness and the size of the area
to be covered
Planning
Planning is
essential in hair transplantation, poor planning can easily lead to unsatisfactory
results which may be impossible to correct. This may be because of unanticipated
progression of hair loss, exhaustion of grafts or missized, misplaced or
misdirected grafts or scars.
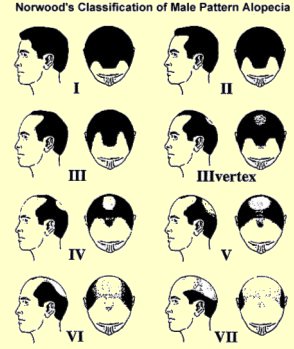
6 Factors
decide patient selection and planning
| 1- Classification
(Exent of baldness)
2- Scalp & hair color 3- Curliness 4- Texture (Caliber) 5- Density 6- Amount of donor hair |
 |
Procedure
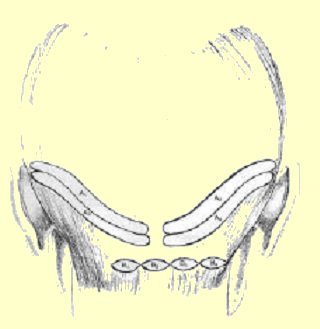
The procedure
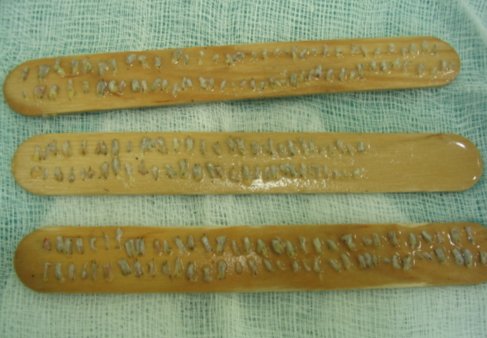
consists of the use of a small 8-mm wide strip of the back of the scalp
removed surgically and closed primarily leaving a fine scar inbetween hairs
which is completely hidden with no areas of alopecia. This strip in dissected
under magnification into hair folliclular units which are then implantated
into the desired ares thourgh small slits in order to leave no scars.
 -
- -
-
 -
-
Bandaging
The area is
covered by bandage for 2 days after which bandage is removed and the area
is washed gently and left exposed. The scabs covering transplanted grafts
should be left undisturbed till they fall spontaneously.
Postoperative
Course
Small crusts
will form over the grafts and usually fall over the first 2 weeks. The
grafts will shed their hairs in 2-6 weeks. New hair growth usually begins
10-20 weeks after surgery and patient should be informed that it would
take at least 6 month postoperatively for hair to grow and to give a good
idea about the final appearance. The use of 2-3 % Minoxidil solution twice
daily for 5-6 weeks postoperatively will often accelerate hair growth.